Innovations fuel the growth and market returns of a firm, making them a critical component of a successful business. However, most innovations fail in the marketplace. The rate is frequently believed to be between 70% and even 90%, endangering the long-term viability of businesses.
This is because most businesses forget to strike a balance between what consumers seek and what this new innovation costs.The balance between attracting customers and covering costs can make or break your business. It’s within this delicate equilibrium that the Gabor-Granger Pricing Method emerges.
It is a valuable tool for businesses striving to understand consumer behavior and optimize pricing strategies.
The pricing of a product or service is a numbers game. It influences your consumer behavior, market positioning, and of course, the success of your enterprise. The essence of pricing lies in finding that sweet spot where customers perceive value, and making a purchase becomes enticing.
The ABC of the Gabor-Granger Method
The Gabor-Granger Pricing Method was introduced by economists André Gabor and Clive Granger in the 1960s. It has since become a trusted companion for businesses navigating the intricacies of pricing research. This method stands out for its simple, yet profound impact in gauging consumer willingness to pay. It also identifies the optimal price points for maximum revenue.
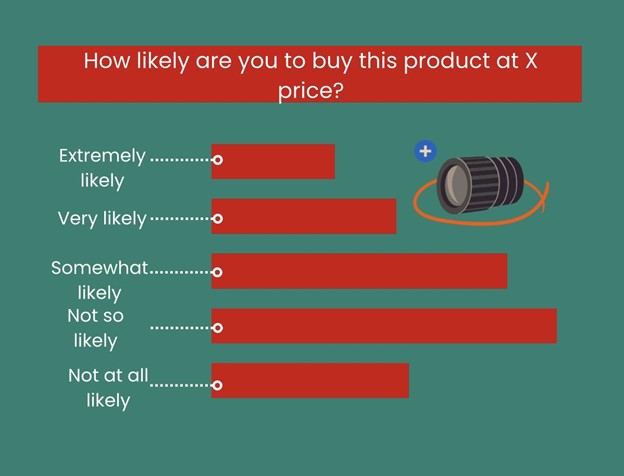
On a five-point scale, respondents only submit one response. The price is reduced and the question is asked again as most respondents provided one of the lowest three answers. The procedure keeps on till the approach determines the highest price that clients are willing to spend.
Researchers create a revenue and demand curve using the data gathered in this way to identify the best price that will generate the most money.

Understanding the Gabor-Granger method involves delving into the psychology of consumer choices. Presenting potential customers with different price points and assessing their likelihood of purchase at each level, crafts a demand curve that guides you towards the most favorable pricing strategy.
The subsequent sections will delve deeper into the intricacies of the Gabor-Granger Pricing Method, exploring when and how to apply it. We also explore the survey setup, results interpretation, and real-life case studies exemplifying its effectiveness.
When to Use Gabor-Granger
Consider applying this method when:
- Directionally Correct Price Estimate. You aim to get a directionally correct price estimate for the willingness of consumers to pay for your product or service. Gabor-Granger provides a realistic understanding of how potential buyers perceive your pricing.
- Optimizing an Established Price Range. You have an established price range, and you seek optimization within that range. This method helps in fine-tuning prices to align with consumer expectations and market dynamics.
- Revenue-Optimizing Price Points. Your goal is to find revenue-optimizing price points. Gabor-Granger identifies the optimum price for maximizing revenue and also constructs a demand curve for deeper insights.
- Change in Price Impact Assessment. You want to determine how a change in price might affect demand elasticity. Gabor-Granger allows businesses to gauge the sensitivity of consumer demand to alterations in pricing.
- Brand-Centric Focus. You prefer to focus solely on your brand without direct consideration of the competition. Gabor-Granger provides a brand-centric view of pricing perception.
Comparison with Other Pricing Methods
While Gabor-Granger shines in certain contexts, it’s valuable to compare it with other pricing methods. This grants you the liberty to choose the right approach for your specific needs. In contrast to methods like Van Westendorp or Conjoint Analysis, Gabor-Granger is particularly suitable for products with an established price range. It is also best for when a brand-centric analysis is desired.
How to Set up a Gabor-Granger Survey?
Launching a successful Gabor-Granger survey involves a thoughtful setup to extract meaningful insights. The questionnaire design plays an active role in obtaining accurate responses. Here’s a brief overview of the key elements in setting up your Gabor-Granger survey:
Question Type Selection
Go to your survey tool. Choose the Gabor-Granger question type from the pricing analysis section. This specialized question type is designed to capture your respondents’ willingness to pay at different price points.
Survey Structure
Decide on the structure of your survey. You can opt for a manual setup if your predetermined price list has varying intervals. Or go for an automatic setup and specify iterations to generate a price list with equal intervals. This flexibility caters to different pricing scenarios.
Striking the right balance ensures a comprehensive understanding of price sensitivity. This helps you pinpoint your optimal price points.
Product Description Inclusion
Enhance your survey by including a concise and compelling product description. This step provides respondents with a clear understanding of the product or service under consideration.
Product description serves as the window through which respondents perceive the offering. Clear, concise, and enticing descriptions attract meaningful responses. This also aligns respondent expectations with the actual product or service.
How to Analyze Gabor-Granger Results?
The analysis phase is where you get all the fun stuff. You get to derive actionable insights and make informed decisions. Here’s a breakdown of the interpretation process:
Demand Chart Insights
The demand chart visually represents your respondents’ willingness to pay for the product across varied price levels. Peaks and troughs in the chart indicate points of interest. This showcases where consumer interest intensifies or wanes in response to pricing.
Price Elasticity Exploration
This evaluates the responsiveness of demand to changes in price. A higher elasticity suggests that consumers are more responsive to price fluctuations. These fluctuations directly impact the volume of sales. Conversely, lower elasticity indicates less sensitivity to price changes.
Revenue-Maximizing Price Points
This insight helps you craft a pricing strategy that aligns with your Consumer Preferences and revenue optimization. The curve illuminates how the demand for the product fluctuates with changes in pricing. The peaks on the curve indicate price points where revenue is maximized.
Now that you know better, balance the need to cover costs with the imperative to attract consumers. This delicate equilibrium ensures your profitability and also sustains consumer interest.

Conclusion
Ready to embark on a pricing journey that aligns with consumer expectations and maximizes your revenue potential? Researchers.me is your platform for seamless survey creation and analysis. Elevate your pricing strategy with confidence.
Take the first step with Researchers.me and unlock the power of Gabor-Granger for your business’s pricing success. Your optimal pricing strategy awaits!

